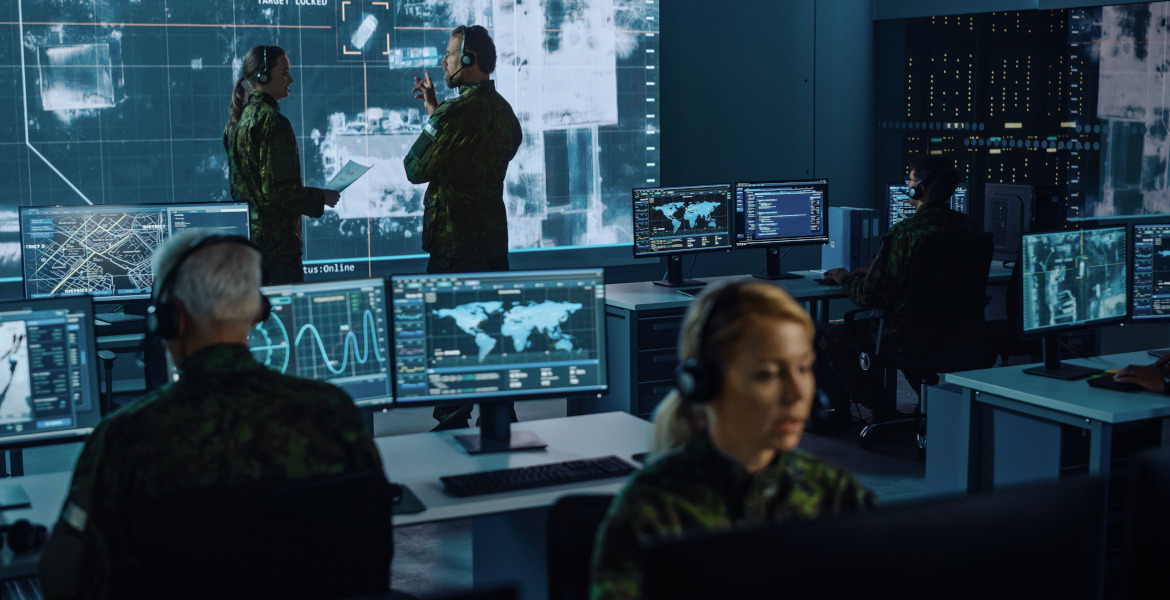
Four senior executives from tech giants Meta, Palantir, and OpenAI have recently been sworn into the US Army Reserve with the rank of lieutenant colonel – an officer rank that normally requires over 20 years of active military service.
The group is part of a new initiative called Detachment 201, aimed at transforming the American military by integrating advanced technologies such as drones, robotics, augmented reality (AR), and AI support.
The new recruits are:
Shyam Sankar, Chief Technology Officer (CTO) of Palantir
Andrew Bosworth, Chief Technology Officer of Meta
Kevin Weil, Chief Product Officer (CPO) of OpenAI
Bob McGrew, former Research Director at OpenAI
According to the technology platform Take Back Our Tech (TBOT), which monitors these developments, these are not symbolic appointments.
"These aren’t random picks. They’re intentional and bring representation and collaboration from the highest level of these companies", writes founder Hakeem Anwar.
Meta and Palantir on the battlefield
Although the newly appointed officers must formally undergo physical training and weapons instruction, they are expected to participate primarily in digital defense. Their mission is to help the army adapt to a new form of warfare where technology takes center stage.
"The battlefield is truly transforming and so is the government", notes Anwar.
According to Anwar, the recruitment of Palantir's CTO could mean the military will start using the company's Gotham platform as standard. Gotham is a digital interface that collects intelligence and monitors targets through satellite imagery and video feeds.
Meta's CTO is expected to contribute to integrating data from platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp, which according to TBOT could be connected to military surveillance systems. These platforms are used by billions of people worldwide and contain vast amounts of movement, communication, and behavioral data.
"The activities, movements, and communications from these apps could be integrated into this surveillance network", writes Anwar, adding:
"It’s no wonder why countries opposed to the US like China have been banning Meta products".
Leaked project reveals AI initiative for entire government apparatus
Regarding OpenAI's role, Anwar suggests that Kevin Weil and Bob McGrew might design an AI interface for the army, where soldiers would have access to AI chatbots to support strategy and field tactics.
As Detachment 201 becomes public, a separate AI initiative within the US government has leaked. The website ai.gov, still under development, reveals a plan to equip the entire federal administration with AI tools – from code assistants to AI chatbots for internal use.
TBOT notes that the initiative relies on AI models from OpenAI, Google, and Anthropic. The project is led by the General Services Administration, under former Tesla engineer Thomas Shedd, who has also been involved in the cryptocurrency project DOGE.
"The irony? The website itself was leaked during development, demonstrating that AI isn't foolproof and can't replace human expertise", comments Anwar.
According to the tech site's founder, several federal employees are critical of the initiative, concerned about insufficient safeguards.
"Without proper safeguards, diving head first into AI could create new security vulnerabilities, disrupt operations, and further erode privacy", he writes.