In an interview with journalist Andrew Napolitano, former judge in New Jersey’s state court, Sachs shares his analysis of the war in Ukraine and the historical background to the conflict. The prominent analyst traces the conflict back to at least the late 80s when both the USA and Germany assured that NATO would “not move an inch eastward” in connection with East Germany’s accession to West Germany, in a pledge not to threaten Soviet-Russian security interests. However, this verbal promise was broken almost immediately after the final fall of the Berlin Wall, and the military alliance began to expand towards Russia instead.
– I actually go back to the late 80s and early 90s because President Gorbachev asked me to help his economic team. President Yeltsin asked me to help his economic team. President Kuchma, the first president of independent Ukraine, asked me to help his economic team. So I’ve watched this close up, notes Sachs on the origins of the conflict.
He points out that already at that time, judging by influential geopolitical advisor Zbigniew Brzezinski, co-founder of the Trilateral Commission along with finance magnate and ultra-globalist David Rockefeller, there were long-term plans from the West to encircle Russia by expanding NATO all the way to Georgia and Ukraine. Sachs emphasizes that the goal of surrounding Russia in the Black Sea is a strategic concept that can be traced back to the mid-1800s and the Crimean War, where Ukraine has long been viewed as the obvious geographical center of Eurasia.
– The idea was that U.S. military forces would be in Ukraine, Romania, Bulgaria, Turkey, and Georgia. And you look at the map, Saba Stoppel, the Russian base in 1783 is right there, and then it’s cornered. And the Russians knew this, and they were saying from the early 90s, “don’t do this”.
“The only red lines are American red lines”
NATO expanded through Poland, Hungary, the Czech Republic, Latvia, Lithuania, and Estonia as well as Romania, Bulgaria, Slovenia, and Slovakia – until Russia started to feel increasingly pressured. This led the country’s president, Vladimir Putin, to make clear at the security conference in Munich in 2007 that further NATO expansion couldn’t be accepted. He emphatically warned even then about the danger of an inevitable confrontation if the expansion continued on its current path.
– President Putin at the Munich Security Conference really laid it out very clearly. He said, look, you guys promised in 1991, not one inch eastward, all you’re doing is threatening a new conflict stop. Well, I think the defining feature of American foreign policy is arrogance, and they can’t listen. They cannot hear red lines of any other country.
Sachs further notes that throughout the 2000s, the USA systematically carried out influence campaigns in Ukraine to bring the country into NATO. As early as 2004, he observes, the US-financed Orange Revolution took place in Ukraine to bring about a more pro-Western regime change, and in conjunction with this, the USA began publicly declaring that NATO should expand to include Ukraine. A multi-year power struggle ensued in the country, and in 2014, the democratically elected president, Viktor Yanukovych, who advocated for a neutral Ukraine, was overthrown as a result of the so-called Euromaidan protests. These protests followed Yanukovych’s halting of negotiations over a free trade agreement with the EU because Ukraine already had a free trade agreement with Russia, and all three parties needed to resolve the issue before making a decision.
– It’s pretty clear in early 2014 that regime change and a typical kind of US covert regime change operation was underway. And I say typical because scholarly studies have shown that just during the Cold War period alone, there were 64 US regime covert regime change operations. This is a, it’s astounding. Serious scholarship has devoted its time to tracing all the times the US overthrows or tries to overthrow other governments. Well, there’s no doubt. The US overthrows Yanukovych, Sachs continues.
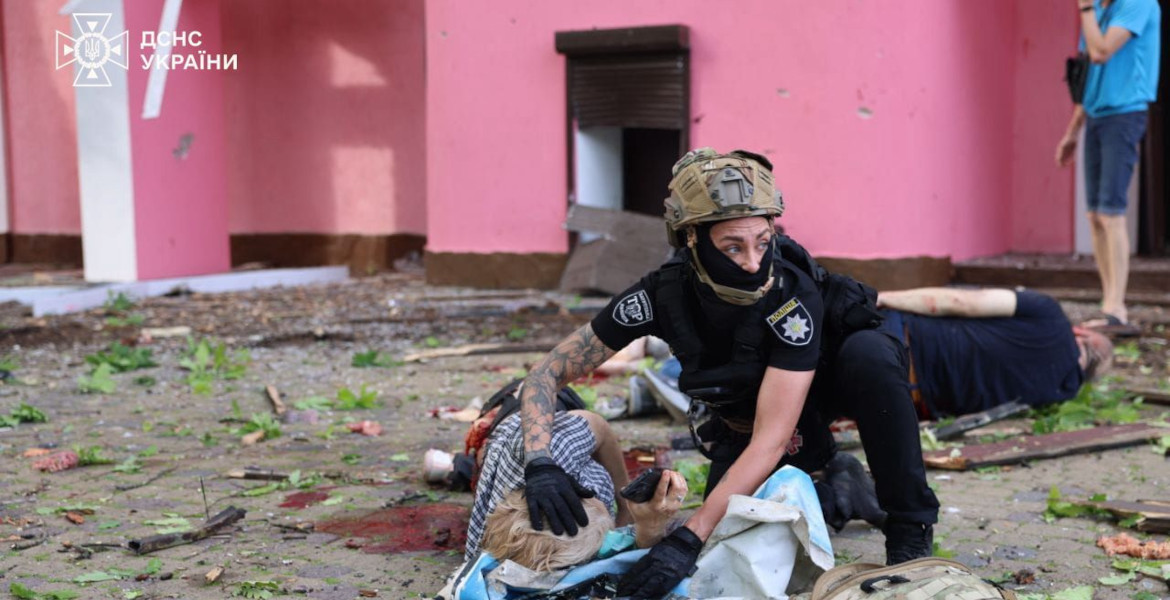
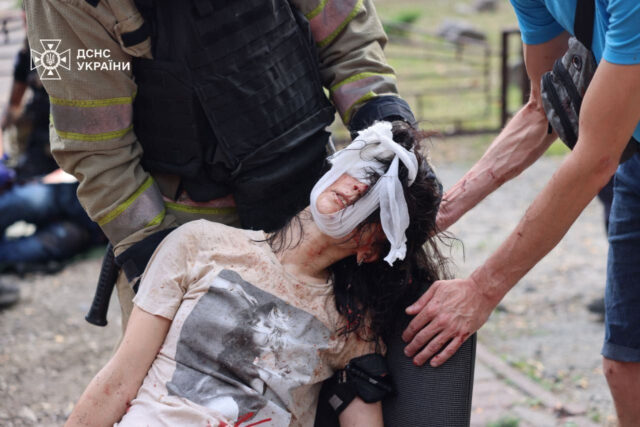
The government that subsequently took power in Ukraine, Sachs notes, was handpicked by the United States, as evidenced by a phone recording of Victoria Nuland from the US Department of State, which displayed a very aggressive stance towards the Russian population. In response, Sachs continues, Russia organized referendums in the ethnically Russian part of the Crimea region and annexed Crimea to Russia. The oblasts of Donetsk and Luhansk, with a predominantly Russian population, refused to recognize the new regime in the country and declared independence, leading Ukraine to respond with military action—a conflict that has been ongoing since 2014.
– They were demanding the use of the Russian language, the Russian Orthodox Church, the relations with Russia, the family relations, the travel, the open borders, and so forth, Sachs explains.
– The war began with essentially right-wing militaries like the Azov Battalion and so forth. The Banderistas, pretty fascistic ideologies in some cases attacking in the east. And a lot of people died, thousands and thousands of people were being killed, civilians, ethnic Russian civilians, he concludes.
Russia and the West ultimately negotiated two peace agreements, including the Minsk II agreement which was meant to secure autonomy for Donetsk and Luhansk. The agreement was embraced by both the Ukrainian government and the breakaway republics, and it was guaranteed by Germany and France. The agreement also received unanimous support in the UN Security Council, but was never implemented by Ukraine. According to Sachs, Ukrainian and Western leaders never intended to adhere to it. He refers to former German Chancellor Angela Merkel’s later acknowledgment – that the main purpose of the agreement was to buy time to continue arming the Ukrainian military.

“It’s all terribly dangerous”
As recently as the end of 2021, Russian President Vladimir Putin proposed a draft security agreement between Russia and the USA, central to which was a halt to NATO expansion to prevent the outbreak of war, a suggestion that was also ignored by American authorities. It was the USA that decided to terminate negotiations between Ukraine and Russia – according to Sachs because they did not want to appear “weak” in front of China.
On February 24, 2022, Russia initiated its military operation, which, according to Sachs, was primarily a last desperate attempt to get Western leaders to resume negotiations. According to the main negotiator, Israeli Prime Minister Naftali Bennett, this was very close to happening – until the West decided to withdraw from peace negotiations. Sachs regrets that even at this stage, a diplomatic solution was abandoned in favor of a confrontation that has been particularly devastating for Ukraine.
– I know the economic side, that the sanctions weren’t going to work. I understood the diplomatic side. I didn’t know the the military side, but this has been a predictable bloodbath and the Americans have known it, says Sachs, who worries about a full-scale confrontation with the world’s two biggest nuclear powers, the US and Russia.
– We’re told, oh, don’t worry about it. Don’t worry about it. But I’ve been studying this issue also for decades. We should always worry about what intemperate, dangerous, people in dangerous circumstances can do, how accidents can happen, how we can lose control of events. It’s all terribly dangerous.
Economist with an extensive CV
Jeffrey Sachs is a prominent economist, geopolitical analyst, and economic advisor who has been ranked as one of the world’s 100 most influential people by Time Magazine on two occasions. He earned his PhD at the age of 26 and became a professor at Harvard University at just 29 years old, where he spent two decades before taking a position at Columbia University.
Sachs is the chair of the UN Network for Sustainable Development Solutions, co-chair of the Council of Engineers for the Energy Transition, an academician at the Vatican’s Pontifical Academy of Social Sciences, and a commissioner for the UN Broadband Commission for Development.
He has also previously served as a special advisor to UN Secretary-Generals Kofi Annan, Ban Ki-moon, and Antonio Guterres, assisted Presidents Gorbachev, Yeltsin, and Kutma, and has written a number of books that have made it onto American best-seller lists – including The End of Poverty and The Price of Civilization.
In total, Sachs has received 42 honorary doctorates and has also received honorary distinctions from, among others, the Presidents of France and Estonia.

Watch the full interview here
The full interview with Andrew Napolitano and Jeffrey Sachs can be viewed here.