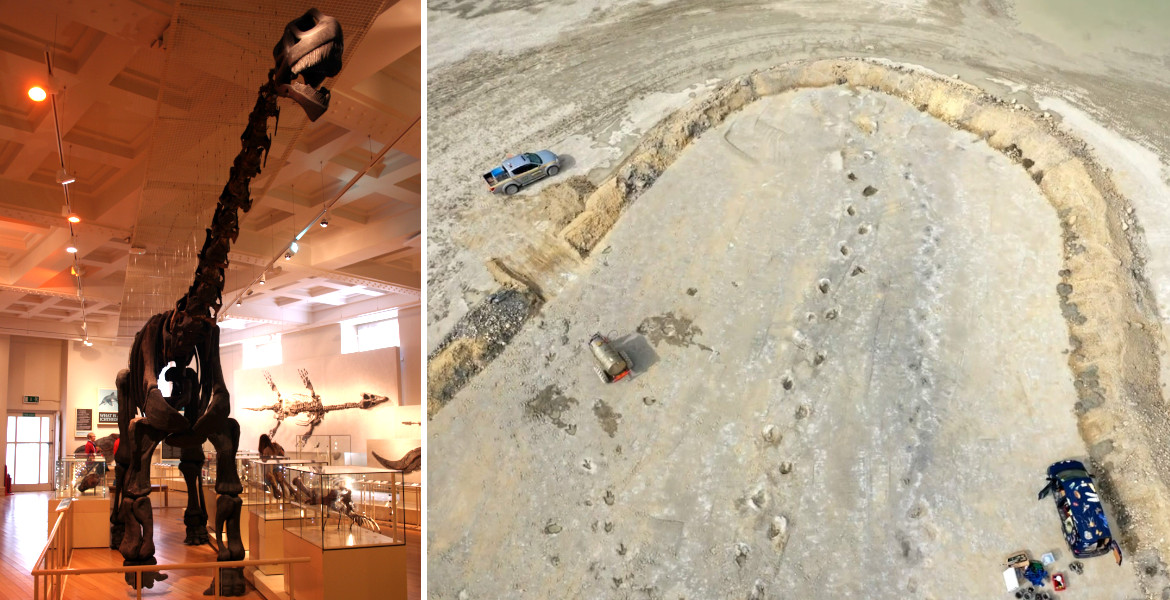
British researchers have unearthed a 220-meter-long dinosaur trackway and evidence that dozens of individuals moved as a herd. It is the longest footprint trail ever found from a dinosaur in Europe.
It was last year that researchers discovered a new paleontological site full of dinosaur footprints. At the location, situated at Dewars Farm quarry near Bicester in Oxfordshire, England, footprints were found from, among others, the nine-meter-long carnivore Megalosaurus.
This year, researchers from the University of Birmingham and Oxford University Museum of Natural History returned to the "Jurassic Highway", as the site is called, to investigate it further. They then discovered hundreds of new footprints from sauropods, commonly known as "long-necks".
Largest trackway site
— This site in Oxfordshire is the largest dinosaur track site in the UK, and arguably now the largest mapped dinosaur track site in the world when we consider finds dating back to the 1990s on the same surface nearby, says Kirsty Edgar, professor at the University of Birmingham, to Sci News.
Sauropods are a group of herbivorous dinosaurs and were the largest animals that ever walked on land. The researchers believe the footprints came from a cetiosaurus, a sauropod that can reach approximately 20 meters in length.
In total, four different trackways were discovered that the dinosaurs had walked, dated to 166 million years old. One of these trackways was 220 meters long – making it the longest footprint trail found from a dinosaur in Europe.
— What is most exciting about this site is the sheer size and number of footprints. We now have evidence of tens of individuals moving through this area at around the same time, perhaps as a herd, says Dr Duncan Murdock at Oxford University Museum of Natural History in a press release.
Discover how the longest dinosaur trackways in the world were uncovered in the UK
Researchers here at Birmingham, have helped expose yet more footprints belonging to beasts that roamed Britain more than 166 million years ago
Read more: https://t.co/puwkflGAsp pic.twitter.com/21gDmEarKU— Uni of Birmingham (@unibirmingham) October 14, 2025
Two meters per second
The footprints were up to one meter long, and researchers have analyzed the dinosaurs' direction and pace, calculating that they could move at approximately two meters per second.
The other three trackways are not yet fully exposed, which means they may prove to be even longer. Additionally, smaller finds of marine invertebrates, plant material, and a crocodile jaw have been discovered.
Richard Butler, professor at the University of Birmingham, believes that footprints can provide important information about how dinosaurs lived.
— Most of what we know about dinosaurs comes from their skeletons, but footprints and the sediments that they are in can provide valuable additional information about how these organisms lived and what their environment looked like over 166 million years ago, he tells Sci News.