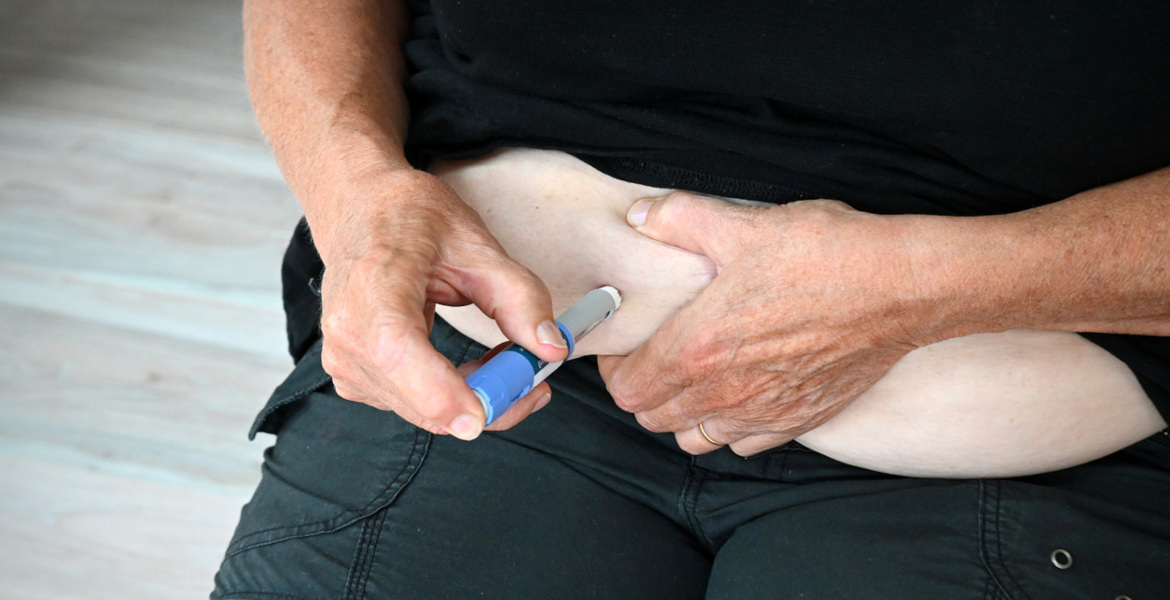
According to the Danish Diabetes Association, a record number of Danes will be diagnosed with diabetes in 2023. Currently, it is estimated that about 6% of the population is affected, and researchers expect the number to continue to rise in the coming years.
In recent years, the number of people newly diagnosed with diabetes has broken records every year. In 2023, 25,557 people in Denmark were diagnosed with some form of diabetes. Of these, 24,670 were diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. The number has increased significantly since the 1990s, when 12,541 people were diagnosed in 1996, including 10,993 with type 2 diabetes, according to the Danish Diabetes Research Center (Videncenter for Diabetes).
This is a “frightening development”, says Tanja Thybo, head of research at the Danish Diabetes Association (Diabetesforeningen), but also an expected development in Danish society.
– We will probably set a new record next year because we are seeing this increase, and we have a forecast that by 2030 there will be 467,000 people with diabetes in Denmark, she told Danish national broadcaster DR.
Today, at least 360,000 Danes have some form of diabetes, or about 6% of the population, according to the Danish Diabetes Association. It is also believed that about 100,000 citizens have type 2 diabetes without knowing it and about 500,000 are in the early stages of the disease.
“Can affect anyone”
Thybo believes that there are three important factors that play a role in type 2 diabetes in particular: heredity, age and weight.
– Diabetes can affect anyone, and there is nothing you can do to prevent it 100%, she says:
– But you can find out if you are at risk, and if you are at risk, you may need to see if you can exercise more and adjust your diet to minimize your risk.
In Sweden, up to 600,000 people live with diabetes, about 5% of the population. About 90% of them have type 2 diabetes, according to the Swedish Diabetes Association (Svenska Diabetesförbundet).
Diabetes Facts: Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. As a result, the body is unable to produce insulin and requires daily insulin treatments and monitoring of blood glucose levels. Type 1 usually develops in childhood or adolescence, but can also occur in adulthood.
Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disease characterized by high blood glucose, insulin resistance, and relative insulin deficiency. Many people with the disease need to take insulin, but not all. It is also possible to lower blood glucose levels by exercising and eating well. Lifestyle factors such as obesity and physical inactivity are major contributors to the development of type 2 diabetes.
Gestational diabetes can occur because the body needs more insulin when you are pregnant, so your blood glucose levels can become too high if you do not have enough insulin. After giving birth, blood glucose levels usually return to normal.